the history of water
-
Aqueducts in Ancient Persia and the Roman Empire
Aqueducts stand as enduring testaments to ancient civilizations' mastery of hydraulic engineering, providing vital insights into their innovative approaches to water management. In this article, we explore the utilization of aqueducts in ancient Persia and the Roman Empire, shedding light on their profound impact on public health, environmental sustainability, and societal development. -
Overview:
Ancient Persia, particularly during the Achaemenid Empire (c. 550–330 BCE), relied on ingenious water management systems to harness nature's bounty and sustain urban centers and agricultural regions. Among these systems, the utilization of aqueducts and qanats played a pivotal role in delivering potable water to communities amidst arid landscapes. -
Design and Construction:
Persian aqueducts, often intertwined with intricate qanat networks, epitomized eco-friendly water sourcing methods. Qanats, vertical wells, and underground channels tapped into subterranean aquifers, ensuring a steady supply of pristine water while minimizing ecological disruption. -
Impact and Legacy:
The advent of aqueducts in ancient Persia transformed the region's socio-economic landscape, fostering urbanization, agricultural prosperity, and public health advancements. The legacy of Persian aqueducts endures in the preservation of ancient hydraulic infrastructure and the continued utilization of qanat systems in modern-day Iran. -
Overview:
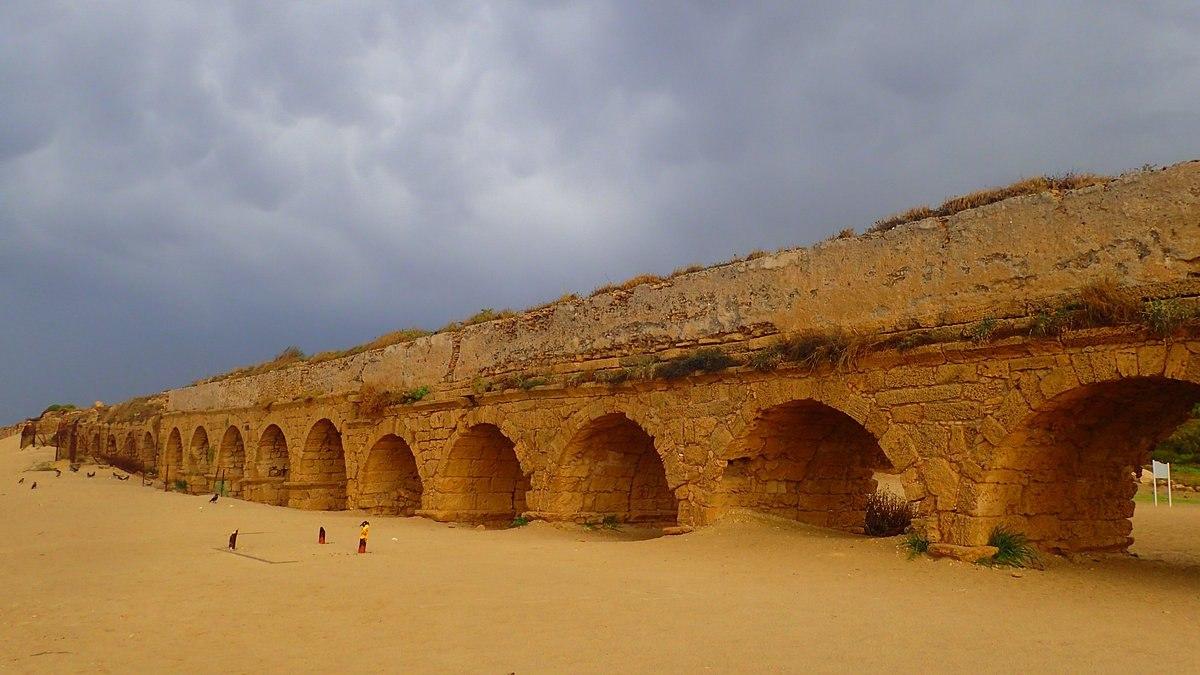
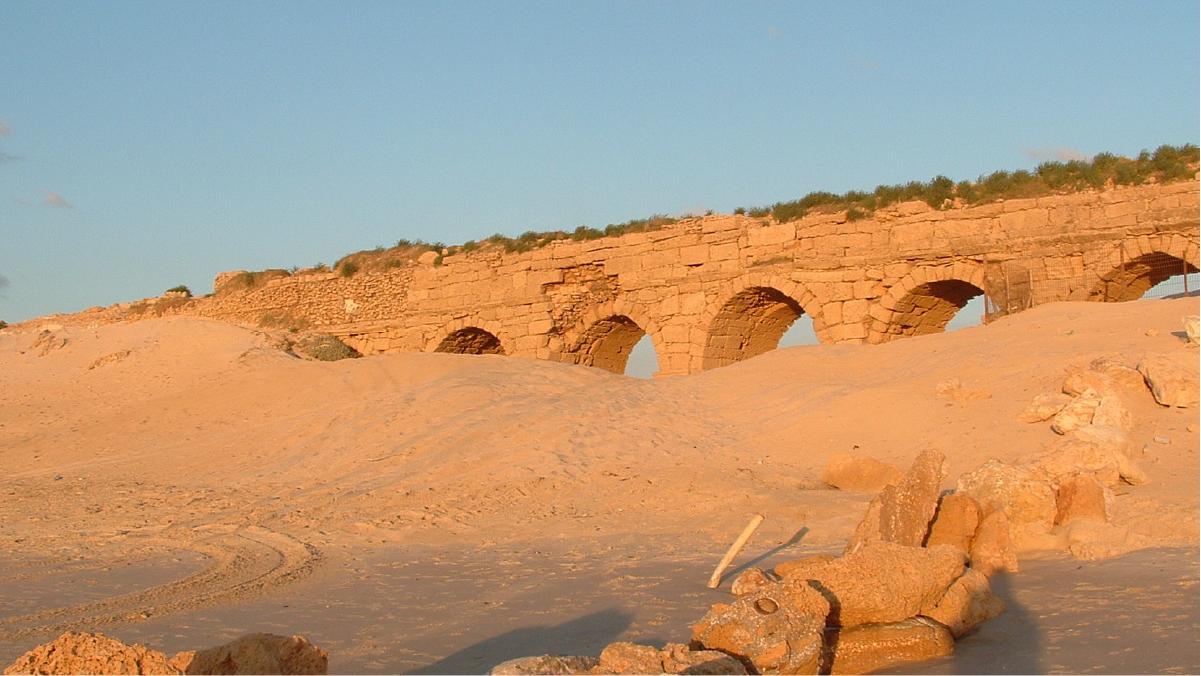
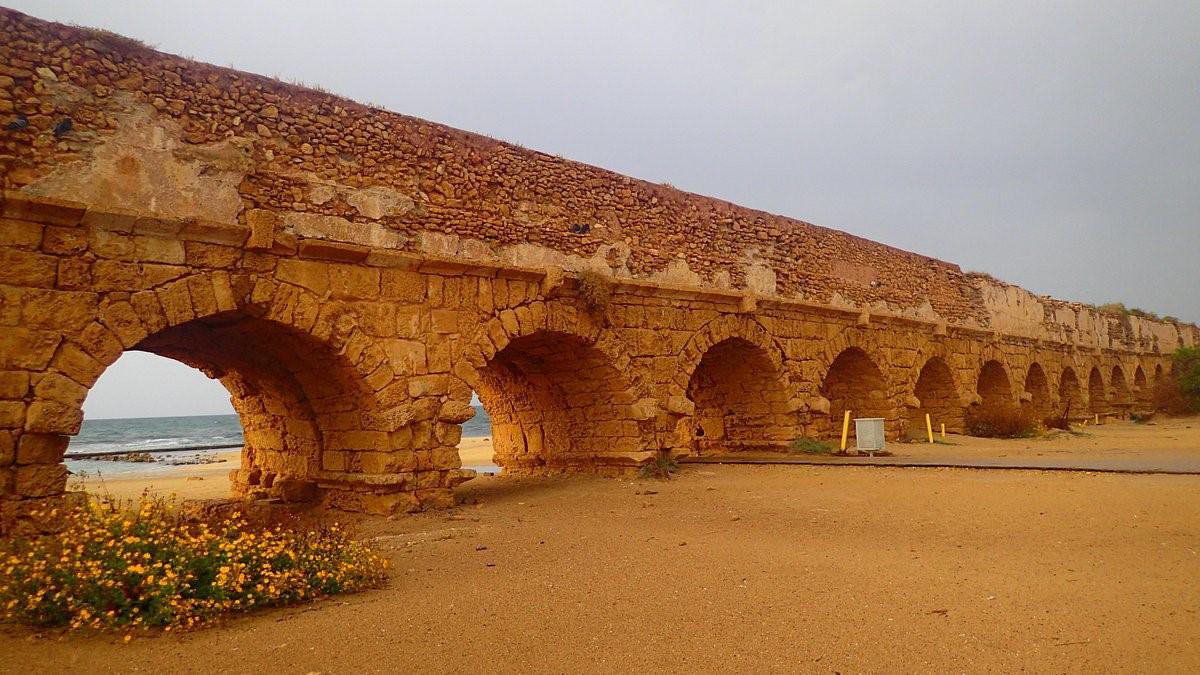
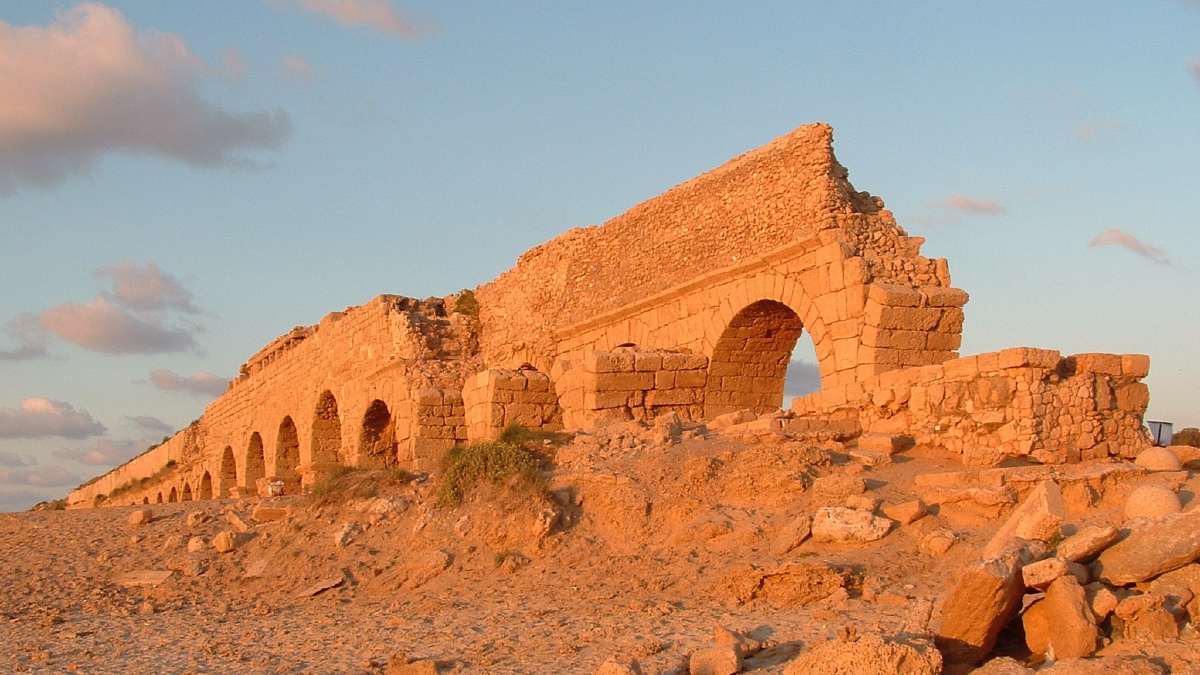
The Roman Empire's aqueducts stand as monumental achievements in hydraulic engineering, revolutionizing urban life and ecological sustainability across vast territories. From the Republican era to the zenith of imperial power, aqueducts symbolized Rome's commitment to public welfare and environmental stewardship. -
Design and Construction:
Roman aqueducts exemplified meticulous planning and architectural prowess, incorporating innovative materials and structural designs. Constructed with precision-cut stone arches and gravity-fed conduits, these aqueducts harnessed the power of natural gradients to deliver potable water to burgeoning cities and rural settlements. -
Impact and Legacy:
The implementation of aqueducts profoundly impacted Roman society, promoting public health, sanitation, and civic amenities such as baths and fountains. The environmental legacy of Roman aqueducts is evident in the preservation of ancient watercourses and the enduring influence of Roman hydraulic engineering on modern urban infrastructure. -
Conclusion:
Aqueducts served as conduits of progress and prosperity in ancient Persia and the Roman Empire, embodying humanity's symbiotic relationship with water and the environment. By harnessing nature's bounty through innovative water management techniques, these civilizations laid the groundwork for sustainable development and societal resilience, leaving an indelible mark on history and the natural world.